In the modern periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons define the identity of an element (i.e., an element with 6 protons is a carbon atom, no matter how many neutrons may be present). The number of protons determines how many electrons surround the nucleus, and it is the arrangement of these electrons that determines most of the chemical behavior of an element.
In a periodic table arranged in order of increasing atomic number, elements having similar chemical properties naturally line up in the same column (group). For instance, all of the elements in Group 1A are relatively soft metals, react violently with water, and form 1+ charges; all of the elements in Group 8A are unreactive, monatomic gases at room temperature, etc. In other words, there is a periodic repetition of the properties of the chemical elements with increasing mass.

In the original periodic table published by Dimitri Mendeleev in 1869, the elements were arranged according to increasing atomic mass— at that time, the nucleus had not yet been discovered, and there was no understanding at all of the interior structure of the atom, so atomic mass was the only guide to use. Once the structure of the nucleus was understood, it became clear that it was the atomic number that governed the properties of the elements.
Atomic Number is the amount of electrons in an atom, it is also the amount of protons in the nucleus of an atom.Example:Oxygen (O) has the atomic number, 8. Which means that there are 8 protons in. The greater nuclear charge attracts the water molecules more and a ligand can be formed. Thus, as the atomic number increases, the metal ion will form a ligand with water molecules more easily, and the dissolved oxygen concentration will decrease as more water molecules will form ligand with the metal ion.
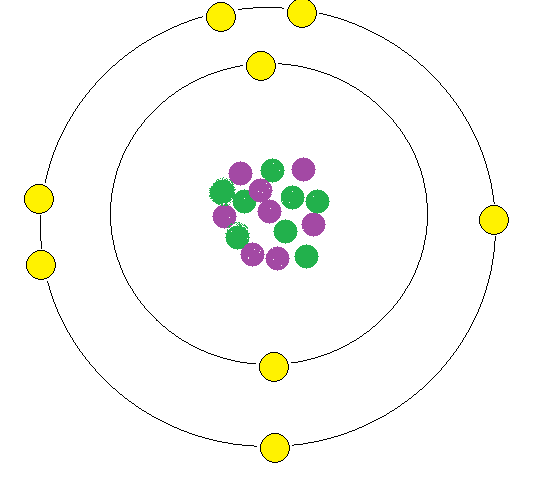
Oxygen is a chemical element with atomic number 8 which means there are 8 protons and 8 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Oxygen is O. Oxygen is a colourless, odourless reactive gas, the chemical element of atomic number 8 and the life-supporting component of the air.

What Is Atomic Oxygen

Oxygen Atomic Number 15
The unit of atomic mass was thereby defined as 1/16 the mass of an oxygen atom. In 1929 it was discovered that natural oxygen contains small amounts of two isotopes slightly heavier than the most abundant one and that the number 16 represented a weighted average of the three isotopic forms of oxygen as they occur in nature. Mass number (A) is the sum of the atomic number(Z), which is the number of protons, and neutrons (N) in the nucleus of a specific isotope of an element (A=Z+N).
